Visual Studio 2015 and Gulp
Having played around with the Visual Studio 2015 preview a bit I've tried to learn how Gulp integrates with the Web Application project.
Gulp seems like one of those many, many, constantly appearing JavaScript libraries with names like YamahaPotplantSaucepan.js which are impossible to keep up with. However since it takes the place of the Bundle config it's important to be able to achieve a basic level of familiarity with it.
What does it do?
Gulp describes itself as a "streaming build system" which basically means you can wire up a pipeline of operations to perform on your content, such as JavaScript and CSS.
By default the project template comes with a gulpfile (shown in the image as #1). This is configured to take the dependencies from Bower (which is a package manager loading a few jQuery packages in by default) and copy them to the wwwroot/lib folder (#3 in the image).
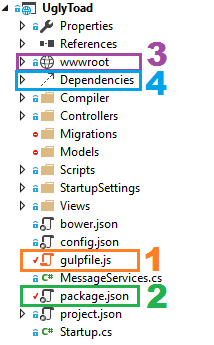
The Bower packages are listed in the bower.json file.
The standard gulpfile looks like this:
/// <binding Clean='clean' />
var gulp = require("gulp"),
rimraf = require("rimraf"),
fs = require("fs");
eval("var project = " + fs.readFileSync("./project.json"));
var paths = {
bower: "./bower_components/",
lib: "./" + project.webroot + "/lib/"
};
gulp.task("clean", function (cb) {
rimraf(paths.lib, cb);
});
gulp.task("copy", ["clean"], function () {
var bower = {
"bootstrap": "bootstrap/dist/**/*.{js,map,css,ttf,svg,woff,eot}",
"bootstrap-touch-carousel": "bootstrap-touch-carousel/dist/**/*.{js,css}",
"hammer.js": "hammer.js/hammer*.{js,map}",
"jquery": "jquery/jquery*.{js,map}",
"jquery-validation": "jquery-validation/jquery.validate.js",
"jquery-validation-unobtrusive": "jquery-validation-unobtrusive/jquery.validate.unobtrusive.js",
"jquery-ui": "jquery-ui/*.{js,map}"
}
for (var destinationDir in bower) {
gulp.src(paths.bower + bower[destinationDir])
.pipe(gulp.dest(paths.lib + destinationDir));
}
});
This script defines 2 Gulp tasks:
- clean - uses a force clean to delete everything in the
wwwroot/libfolder (rimraf is a npm package which recursively force deletes all files in the target folder, equivalent to therm -rfcommand). - copy - runs a clean first and then copies the scripts from their Bower package location to the
wwwroot/lib/NAMEfolder, where NAME is the left hand of thebowerjson object.
How do I run it?
The Gulp tasks can be run manually from the Task Runner Explorer (if you can't see it go to Views > Other Windows > Task Runner Explorer). The result of running the copy task is shown below:
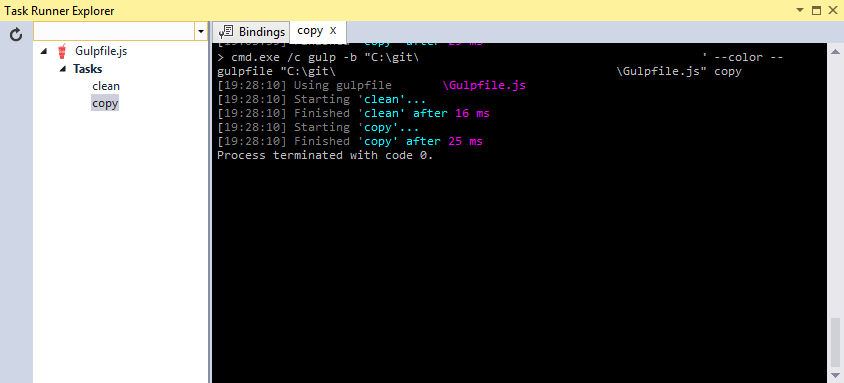
The left hand side has the 2 tasks listed, clean and copy. Right click a task and click "Run" to run it. Tasks can also be bound to some defined bindings, for example you may want to copy on every build:
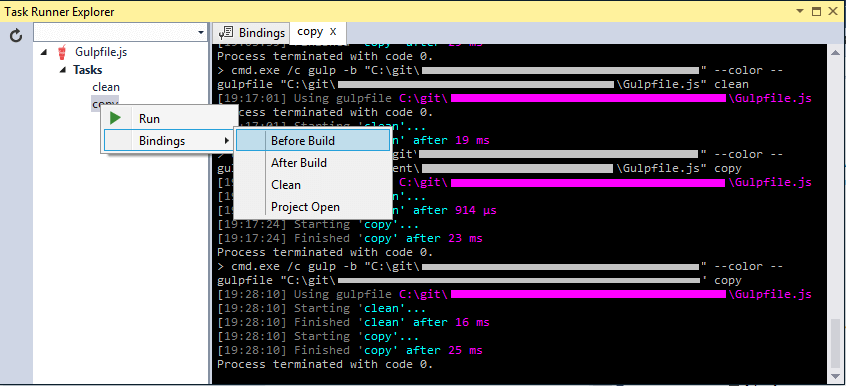
How do I modify it?
In order to use our own files with Gulp we need to modify the Gulp task or write a new one. There are good guides on using Gulp to build a pipeline. This blog post isn't one of them.
We have a folder we use to write all our custom Javascript in, for this tutorial this is in ProjectRoot/Scripts. First we can define this path as a JavaScript variable, I stole space in the pre-defined paths object:
var paths = {
bower: "./bower_components/",
lib: "./" + project.webroot + "/lib/",
scripts: "./Scripts/"
};
The . is the project root.
Since I don't want to be running multiple tasks where I only need one I'm going to put my code in the copy task:
gulp.task("copy", ["clean"], function () {
var bower = {
"bootstrap": "bootstrap/dist/**/*.{js,map,css,ttf,svg,woff,eot}",
// The rest of the bower paths
}
for (var destinationDir in bower) {
gulp.src(paths.bower + bower[destinationDir])
.pipe(gulp.dest(paths.lib + destinationDir));
}
// Copy all project scripts into the lib folder.
gulp.src(paths.scripts + '**.js')
.pipe(gulp.dest(paths.lib));
});
This takes all my scripts from the source (./Scripts folder), it then pipes them into the destination operation which writes them into the ./wwwroot/lib folder.
Note - if the scripts don't show up, look at the lib folder in the Windows File Explorer; Visual Studio sometimes doesn't show the copied Gulp files.
Now we'd like to minify these files, luckily for us we can add a step to our streaming operation.
First we need a component to do the minification. We'll use the node package gulp-uglify to do this. To install this package open the Package.json folder (#2 from the first picture). Put a line in there to reference the uglify package:
{
"name": "ASP.NET",
"version": "0.0.0",
"devDependencies": {
"gulp": "3.8.11",
"rimraf": "2.2.8",
"gulp-uglify": "1.2.0"
}
}
This will cause the node package manager to automatically restore these dependencies. We can now use this in our gulpfile. Modify the top of the gulpfile to include the uglify component:
var gulp = require("gulp"),
rimraf = require("rimraf"),
fs = require("fs"),
uglify = require("gulp-uglify");
Finally you can change the custom code in the copy task to add an Uglify step to the pipeline:
// Copy all project scripts into the lib folder.
gulp.src(paths.scripts + '**.js')
.pipe(uglify())
.pipe(gulp.dest(paths.lib));